What is a Clinical Audit Cycle?
10 March 2022
Tags:
Introduction to Clinical Audit Cycles in Healthcare
Clinical audits are crucial in healthcare for maintaining and improving the quality of care provided by organisations, including both private entities and NHS Trusts.
Their primary goal is to identify areas of excellence and highlight where improvements are needed to enhance patient outcomes. Clinical audits come in two forms: national and local.
This blog delves into the definition, importance, and stages of the clinical audit cycle, providing insights into how these audits function and their impact on care quality.

What is a Clinical Audit?
In 2002, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) defined a clinical audit as:
“A clinical audit is a quality improvement process that seeks to improve patient care and outcomes through systematic review of care against explicit criteria and the implementation of change. Aspects of the structure, processes, and outcomes of care are selected and systematically evaluated against explicit criteria. Where indicated, changes are implemented at an individual, team, or service level and further monitoring is used to confirm improvement in healthcare delivery.”
The Clinical Audit Cycle: Enhancing Healthcare Quality
The clinical audit cycle consists of four stages: establishing best practices, measuring performance against benchmarks, implementing improvements, and continuous monitoring to sustain progress.
Radar Healthcare’s innovative software integrates seamlessly into your clinical audit cycle, supporting every aspect to drive improvements in care. Whether conducting audits in the NHS or private services, our flexible audit tool adapts to your needs.
Now, let’s explore the four stages in detail…
1. Determine best practice
2. Measure against benchmarks
3. Actively work towards improving care
4. Sustain improvement
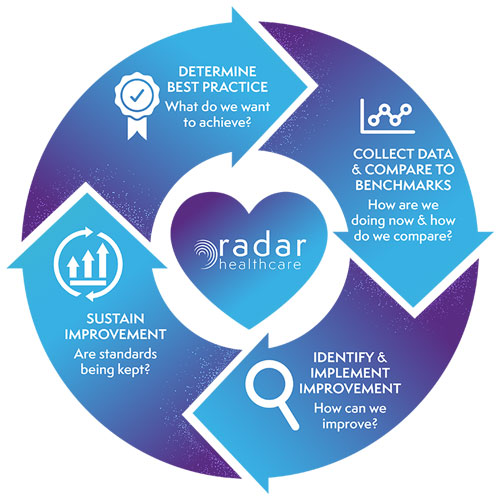
4 Clinical Audit Stages
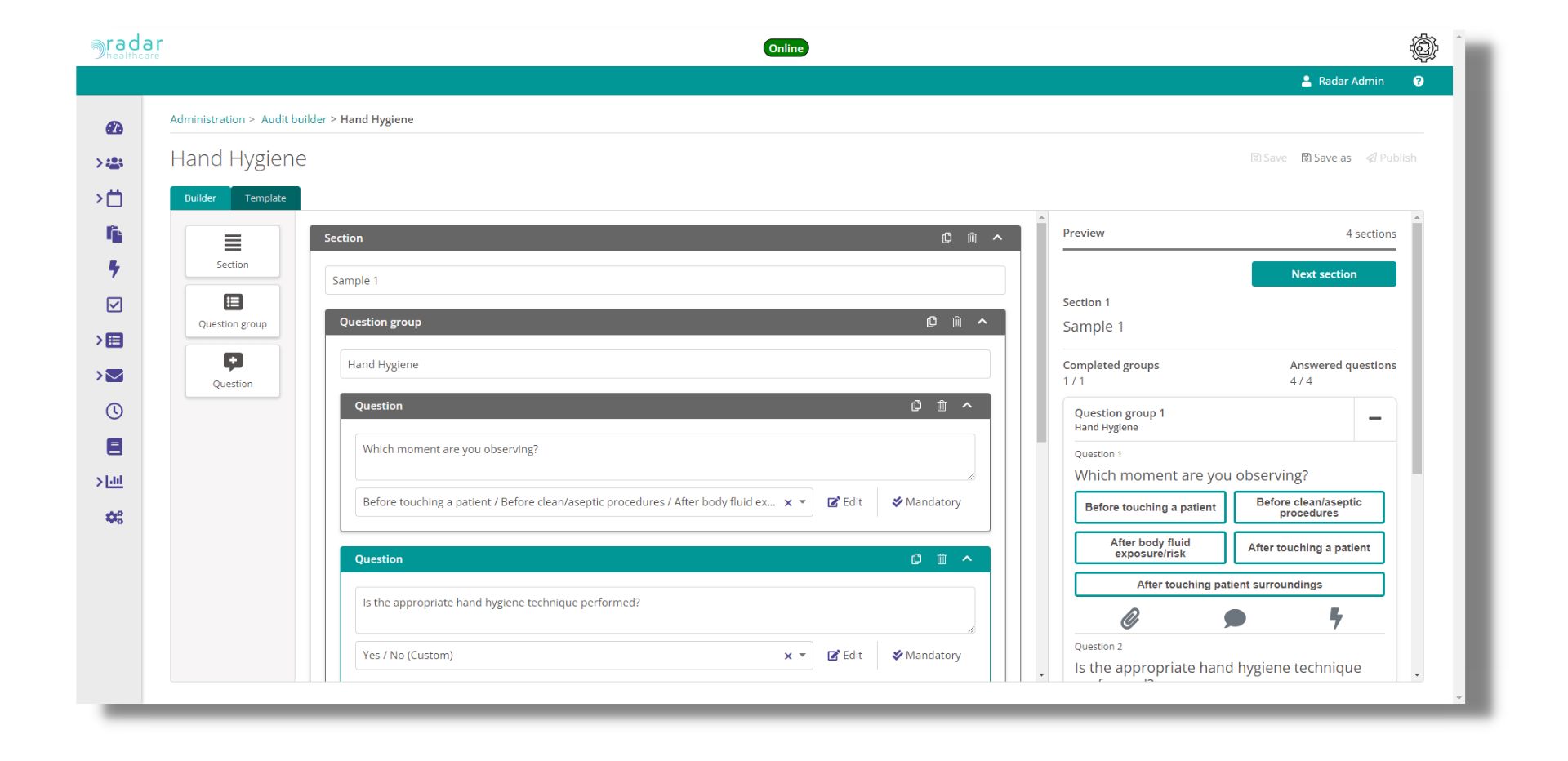
1. Determine best practice
Ask yourself, what do we want to achieve from our clinical audit?
- Every clinical audit should be clear on what the aim for quality improvement is, along with solid objectives.
- Performance should be measured against the best available evidence which is referenced.
- Every staff member in the team delivering the audited service should be told about the project from the start.
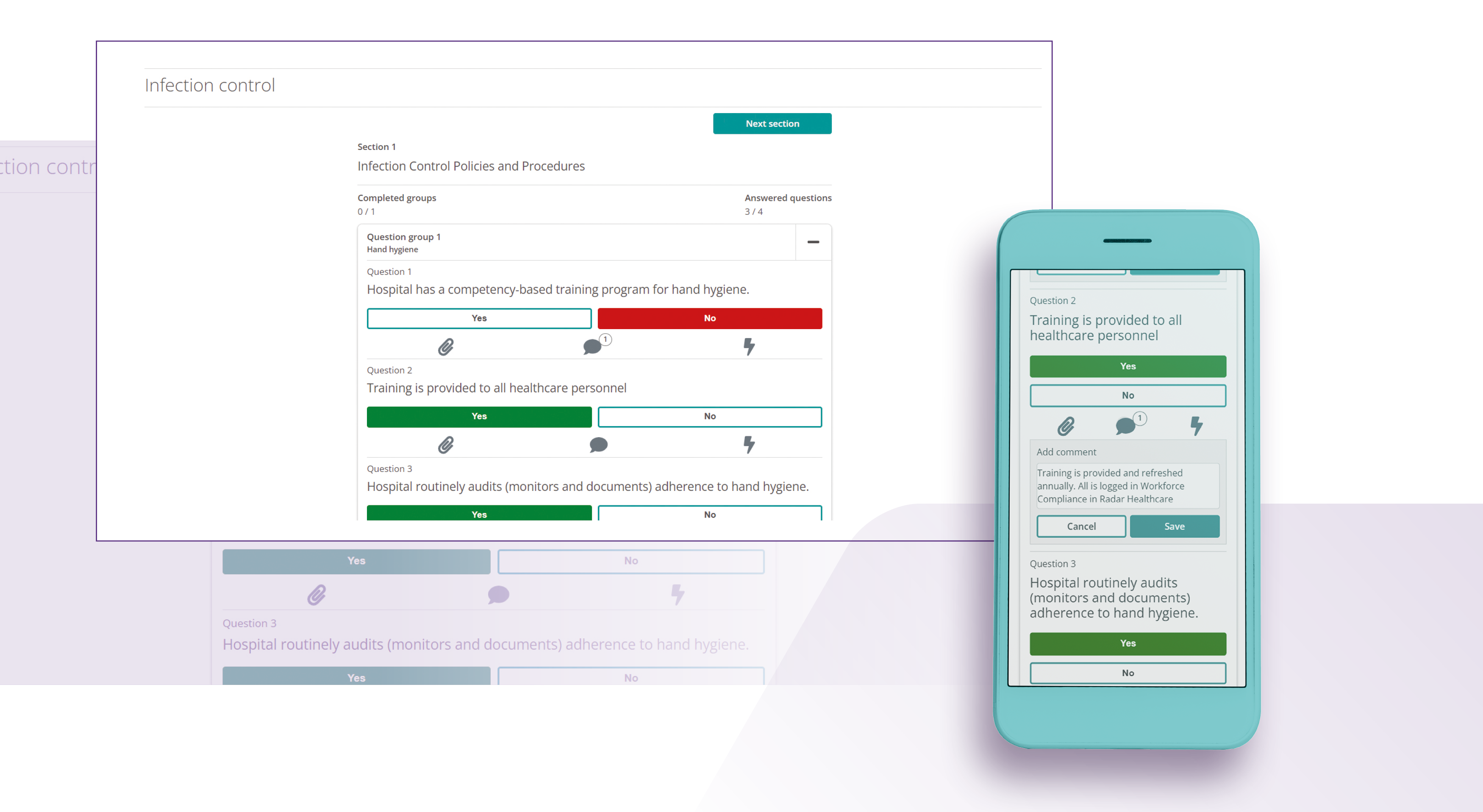
Radar Healthcare’s Document Management module allows you to store all your policies in one place and link these with associated audits.

2. Measure against benchmarks
Ask yourself, how are we performing now and how do we compare to industry benchmarks?
- Only data required to measure compliance with audit standards should be measured.
- The data collected should be analysed to measure compliance with standards, in a clear way.
- Full details must be recorded so if any repeats are necessary, they can be carried out in exactly the same way.
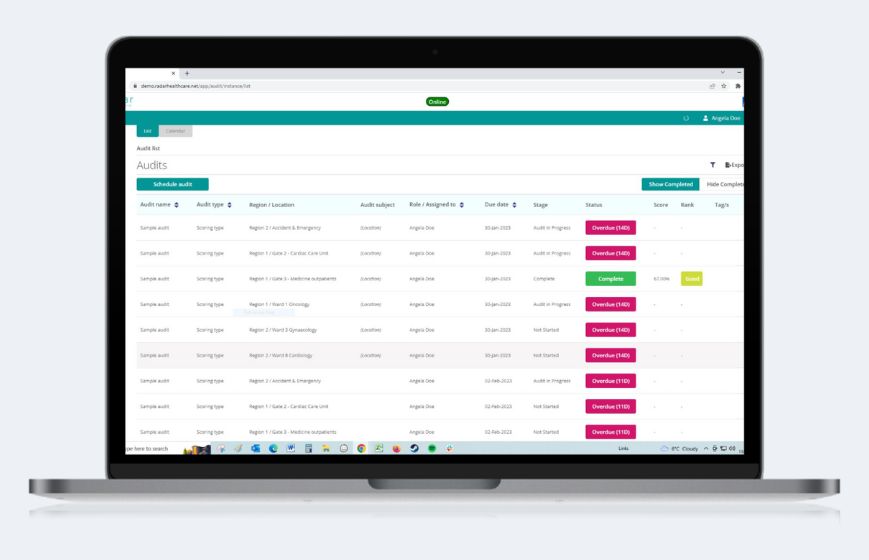
Radar Healthcare’s Audit Management module allows you to create any clinical audits you need to complete. Assign ownership and schedule any re-occurrences so you can be sure that nothing gets missed. You can clearly see audit results in the analytics dashboards for comparison against benchmarks.
One of our customers, Spark Medical said “Radar Healthcare has saved us 4 hours every month on clinical audits, with the added benefit of no admin help being required, meaning we can focus more time on providing care.”

3. Actively work towards improving care
Ask yourself, how can we drive improvements?
- Results should be shared with stakeholders. If non-compliance is presented, underlying causes must be found.
- An action plan must be created to address any underlying causes. System improvements should be proposed to reduce these.
- The action plan must be actioned and the results monitored.
Easily spot which questions have been failed in your clinical audits with Radar Healthcare. The Analytics module has dashboards for complete oversight of audit outcomes, including one for failed results so you can see which particular questions are being failed on.
When the result of an audit is not to standard, Radar Healthcare will instruct relevant staff to begin the necessary action plan. In your action plans, you can see next to each action how many failed audit questions it is linked to, allowing you to prioritise for improvement.

4. Sustain improvement
Ask yourself, are we keeping our standards?
- The audit cycle is only complete once there is evidence to show that the action plan resulted in an improvement in the quality of services.
- Stakeholders must determine if an audit needs to be repeated to sustain any improvement.
- Ongoing monitoring should be established.
- Audit results and action plan outcomes should be documented and shared with the organisation, as well as service users and the public.
- Shared learning is encouraged with people both in the organisation, and associated groups like commissioners and clinical networks.
Radar Healthcare’s analytics dashboards allow you to track trends over time, and you can set up notifications that align with your KPIs. For example, if an audit score is below 80%, relevant staff members get notified so that they can take action to bring the score back up and sustain improvement.
Predictive analytics also forecasts future audit score outcomes from historic data, meaning you can predict how the scores will look in the future.